This article authorizes the reprint from the WeChat public number: Medical Mike
On March 29, 2019, the National Health and Health Commission issued a report on the “Cellular Therapy Clinical Research and Transformation Application Management (Trial) (Consultation Draft)â€, which caused great repercussions among many practitioners in the industry. This scene also appeared about a month ago (February 26), and the National Health and Health Commission also issued the "Biomedical New Technology Clinical Application Management Regulations (Draft for Comment)." The main focus of the two regulatory documents is cell therapy, or more specifically, somatic cell therapy.
After the Wei Zexi incident, the clinical charging application of somatic cell therapy was stopped and unified into the scope of clinical research for standardized management. Subsequently, the Health Planning Commission and the CFDA jointly issued the "Methods for the Management of Stem Cell Clinical Research", followed by the "Guidelines for Quality Control and Preclinical Research of Stem Cell Preparations", following the implementation of stem cell clinical research, such as applying for drug registration. In clinical trials, the clinical research results obtained can be submitted as technical submissions and used for drug evaluation. Then, in 2016, the Food and Drug Administration issued a draft of the "Guidelines for the Research and Evaluation of Cellular Preparation Technology", and in December 2017, it was revised to the "Technical Guidelines for Research and Evaluation of Cellular Therapeutics (Trial)". Later, with the acceptance of the first IND and the approval of the Nanjing Legend, more than 20 domestic companies have filed IND declarations for CAR-T cell products in accordance with the principles of medicines.
Cell therapy is managed according to medical technology or drugs, and varies from country to country. This is due to the differences in management systems in various countries. With the 2017 US FDA Expert Advisory Committee passing the first CAR-T therapy with a 10:0 vote, paving the way for cell therapy in accordance with drug regulation. However, given the specificity of cell therapy products, there are many differences in the regulation of somatic cell therapy, such as clinical research and clinical application of CAR-T cell therapy, according to drug or technology regulation, regulatory subjects and evaluation criteria for clinical research. How medical institutions conduct clinical applications consistent with the GCP principles of medicines, ethical regulatory principles and whether patients benefit from maximization. These issues are currently not explained in more detail in the regulations that have been introduced.
Below we will elaborate on the more prestigious United States, the European Union and Japan, hoping to get inspiration from it.
Product concept definition
The United States categorizes cells, tissues, or cell-based, tissue-based products (HCT/Ps), the European Union is regulated by advanced therapy medicinal products (ATMP), and Japan is regulated by regenerative medicine products.
The United States, the European Union, and Japan have different priorities for the definition of cell therapy products. The United States focuses on defining pharmaceutical methods; the EU focuses on clinical applications, can be used for disease prevention, diagnosis, or treatment, and emphasizes treatment and biology. Characteristics; Japan emphasizes that the source of cells is autologous or homologous, artificial genetic manipulation techniques for cells and are mainly used for treatment and regeneration. Therefore, it can be concluded that the definition of product for cell therapy can be restricted from the source of the cell, the technical scope of the cell manual operation, the pharmaceutical method, and the scope of clinical application.
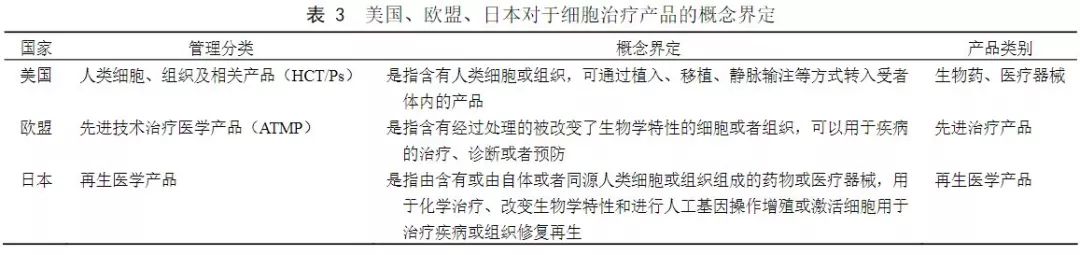
(Source: "China Medical Biotechnology")
Cell therapy approval regulatory policy framework
Although the functions of health and drug regulatory management systems vary from country to country, from the perspective of supervision and approval, cell therapy products and clinical applications are generally divided into two paths:
The first is the regulatory approval of clinical access and application by the drug regulatory authorities for drugs or medical device products, and the process of drug product approval must be strictly followed;
Second, medical technology is supervised by the health department, and clinical applications are directly applied in hospitals. The types and applications of cell treatment defined by different national regulations are different.
1
Japan
Japan’s “regeneration†boom is based on a series of drug reforms and new laws, in particular the landmark Medicines and Medical Devices Act (PMD Act) and the Regenerative Medicine Safety Act, which provide conditional marketing approval for regeneration. It is therefore possible to achieve faster commercialization, which is widely regarded as the fastest approval process in the world.
In Japan, cell therapy, gene therapy, and tissue engineering were separately regulated as regenerative medicine products independent of drugs and medical devices, and in 2013, the approval reform of regenerative medicine products was carried out. In 2013, Japan introduced regulations on the management of cell products, classifying cell products into new categories: products such as regenerative medicine. This management method stipulates that for products such as regenerative medicine with different homogeneity, if the safety can be determined and its effectiveness can be estimated, it can be recognized by additional conditions and deadlines, especially at an early stage. Then re-verify its security and effectiveness. This change in policy has once again made a big step forward in the management of personalized medicine.
The main national regulatory ministries in the field of regenerative medicine are: Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, and Medical Devices (PMDA). The four agencies have different emphasis and division of labor on specific matters such as research promotion, design development, license recognition, quality evaluation, and program review. In addition, the Japan Standards Association (JSA) is responsible for the development of industry standards such as safety evaluation.
Major organizations such as the Reproductive Medicine Innovation Forum (FIRM), the Japan Reproductive Medicine Society, and the Kyoto University iPS Cell Research Institute (CiRA) have also developed industry guidance documents on specific technical aspects such as cell collection, preparation, transportation, and preservation.
Since 2010, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry has developed some guidelines for cell culture related equipment and process flow. In recent years, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare has led many regulations, and has made detailed regulations for different disease areas and cell types, and is also the main reference standard for evaluation and review.
There are two approaches to the clinical development of research medical products in Japan (dual track system): registration trials and clinical studies . A registration test is a clinical trial conducted for the purpose of marketing approval. Clinical studies are not used for marketing approval. The registration test was conducted not only by the company, but also by a registration test initiated by academic researchers as a researcher. In clinical studies, doctors apply medical products to patients as research. Registration trials and clinical studies are subject to different regulations.
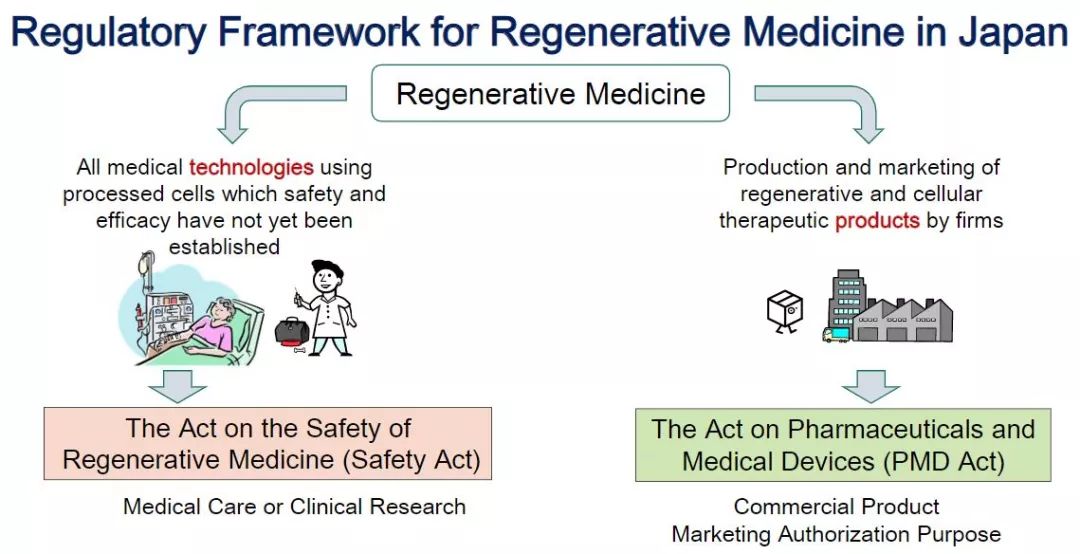
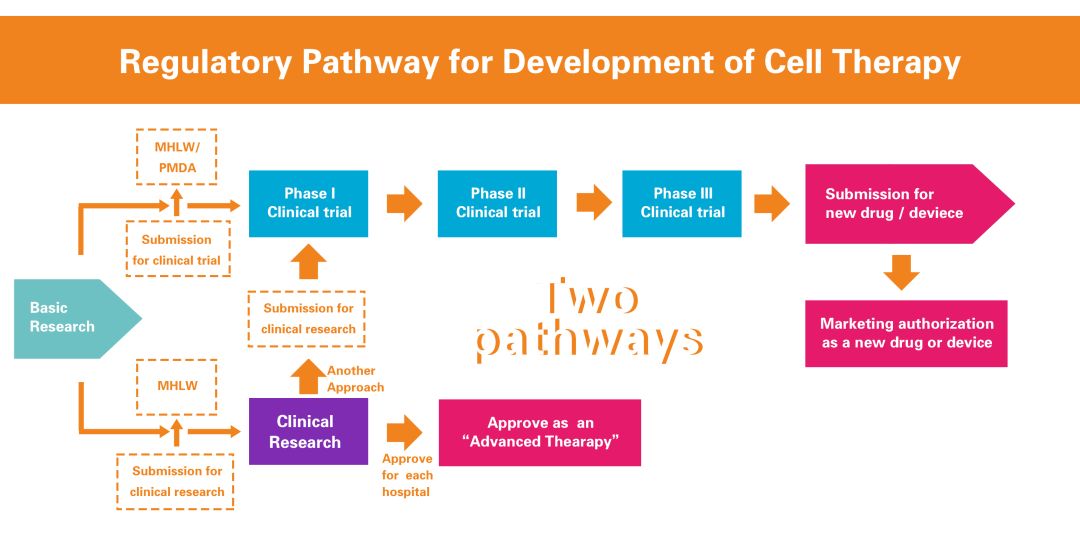
Japanese Regenerative Medicine Regulatory Framework (Source: PMDA, iGEM 2016)
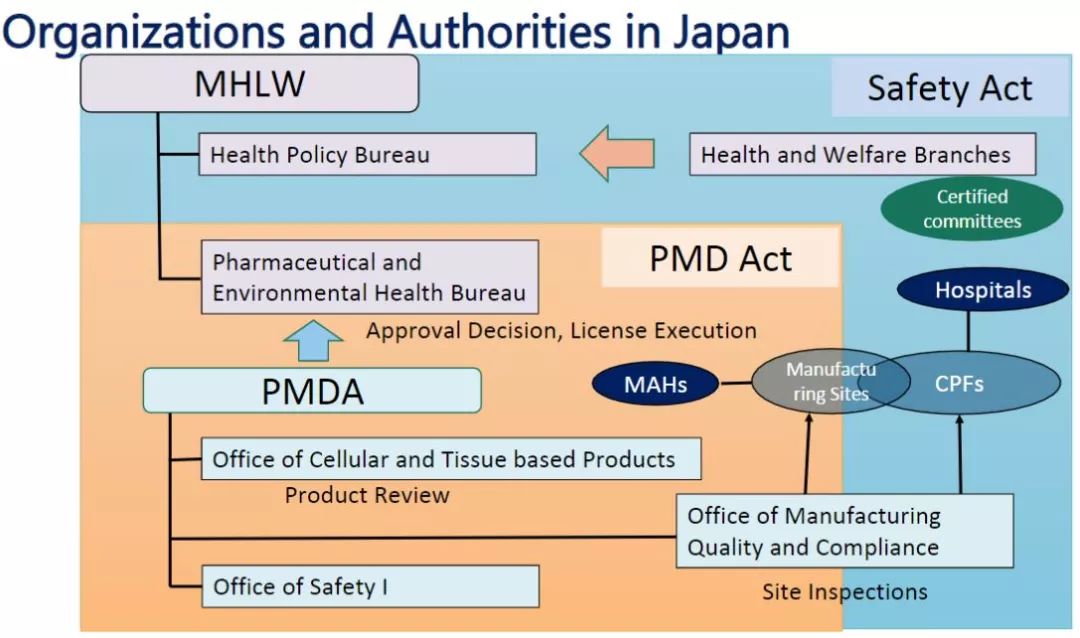
Organization and management (Image source: PMDA)
In terms of registration trials and marketing approvals, the Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Administration (PMDA) reviews research-based new drug notifications for registration trials and marketing approval applications, and the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) approves marketing approvals for pharmaceutical, medical device and regenerative medicine products. In clinical research, MHLW is primarily responsible for regulation, and PMDA is only responsible for the investigation of cell processing facilities.
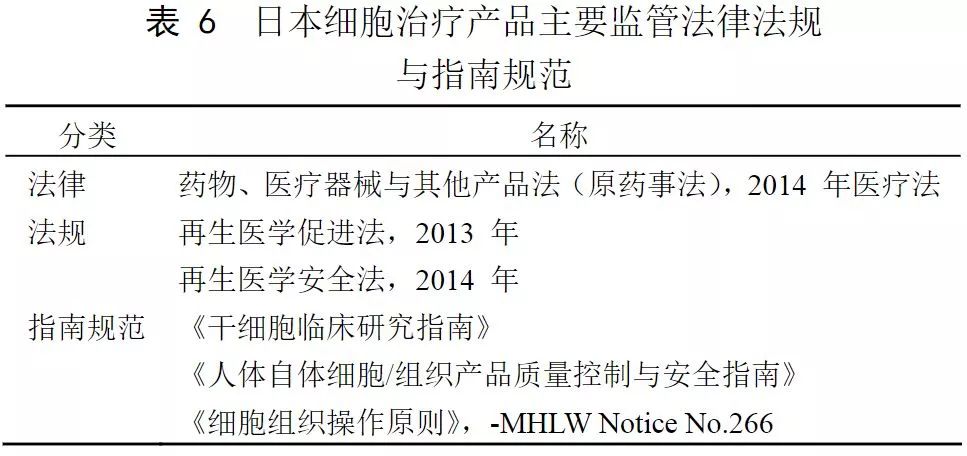
(Source: "China Medical Biotechnology")
(1) Registration test
In November 2014, the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare (MHLW) revised the old Pharmacy Law and implemented the new Medicines and Medical Devices Act (PMD Act), which is applicable to the registration test for marketing licenses. In the Act, cellular medical products, isolated genetic medical products, and in vivo genetic medical products are newly defined as "regenerative medicine products."
Regenerative medicine products are supervised by PMDA under the Medicines and Medical Devices Act. The Drug Evaluation Center has a Cell and Tissue Product Approval Office responsible for specific approval matters. On the basis of the basic research, clinical research, clinical trials and trial approval of the original drug approval procedures, the regenerative medicine products have added conditional restrictive access permits after clinical research has confirmed the effectiveness and safety of regenerative medicine products.
The approval system is similar to the accelerated approval system in the United States and the conditional approval system in the European Union (applicable only to initial marketing approvals). Regenerative medicine products need to meet the following conditions: indications are life-threatening diseases, treatment methods are innovative products that meet the needs, and have passed preliminary validation, safety verification, and compliance with relevant regulatory policies. After the patient's informed consent, the product enters the market, which greatly accelerates the process of clinical application of the product.
Conditional restricted access permitting time is up to 7 years. After proving the clinical trial and application effectiveness of cell therapy products, the product can be applied for long-term listing as a formal regenerative medicine product, and apply again or withdraw after 7 years of expiration. market. At present, a skeletal muscle cell product for severe heart failure of ischemic heart disease has entered the market through conditional restrictive access, with a market investigation period of 5 years.
In addition, MHLW established the SAKIGAKE (for the pioneer or pioneer of Japanese) drug designation system in April 2015. In July 2015, MHLW launched the SAKIGAKE designation system for medical devices, in vitro diagnostics and regenerative medicine products.
SAKIGAKE specifies:
Claim
1. The way of action is innovative
2. Serious indications
3. Expected results are significant
4. Medical products are developed in Japan, and the sponsors plan to submit a marketing license application in Japan first.
benefit
1. Priority consultation (reduce waiting time)
2. A large number of pre-application consultations
3. Priority review
4. Assign PMDA managers as concierges
The total review time for SAKIGAKE-designated drugs and medical devices is 6 months (not applicable to SAKIGAKE-designated regenerative medicine products). In general, the total review time for genes and cell products is 9 months; the review time does not include when the company is preparing to respond to PMDA queries. This SAKIGAKE designation is similar to the US breakthrough treatment designation and the EU PRIME (Priority Drug).
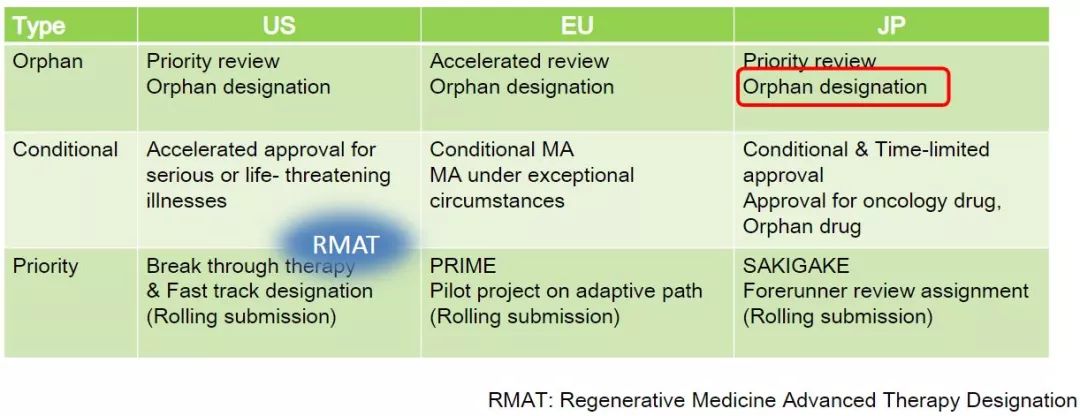
Early Review Promotion Plan (Source: PMDA)
In addition, MHLW launched the Project for Enhanced Practical Application of Innovative Drugs (Medical Devices and Regenerative Medical Products) in 2012 to promote cooperation between PMDA and academic institutions. Regulatory guidance document for innovative medical product evaluation. As planned by MHLW, the project was completed on March 31, 2017.
(two) clinical research
In November 2014, MHLW issued the Regenerative Medicine Safety Act (ASRM) for clinical research outside of the registration test using cell medical products. Therefore, in vivo gene therapy is not within the scope of ASRM, although the regenerative medicine products defined in the PMD Act include in vivo gene therapy. In vitro gene therapy, such as adoptive immunotherapy with gene transfer, falls within the scope of ASRM.
Under the Act, medical or clinical research programs are reviewed by a certified committee and mandatory submissions are made to the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW).
In clinical studies involving in vivo gene therapy, physicians must follow the Guideline on Clinical Research Using In Vivo Gene Therapy. Some (but not all) registration trials and clinical studies of in vivo or ex vivo gene therapy in Japan are listed on the website of the National Institute of Health Sciences.
Under the supervision of ASRM, clinical studies using processed cells are classified as either Class I (high risk), Class II (medium risk) or Class III (low risk). The use of embryonic stem cells, induced pluripotent stem cells, genetically modified cells, animal cells or allogeneic human cells is classified as class I; administration of autologous cells to organs similar to the administered cells (homologous use) is classified as III Class; uses that use autologous cells for other purposes are classified as Class II.
Currently, any Class I and II medical treatment or clinical studies involving ex vivo gene transfer are subject to review by the Osaka University Regenerative Medicine Accreditation Special Committee. The committee can only review the use of clinical studies involving ex vivo gene transfer in any Japanese hospital.
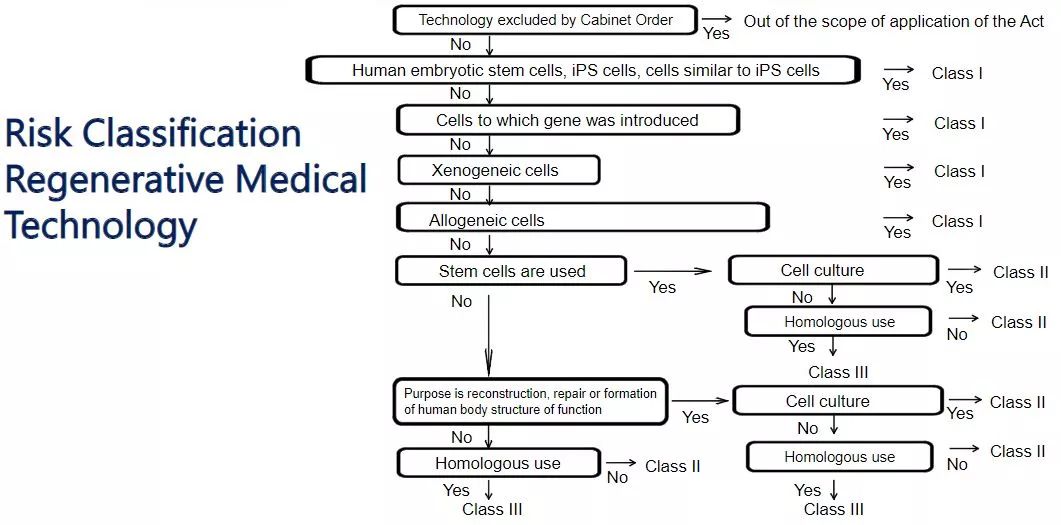
Regenerative Medical Technology Risk Classification (Source: PMDA)
The Clinical Trial Act, which came into effect in April 2018, provides for procedures for conducting “specific clinical trialsâ€, measures for the proper functioning of the Certification Review Committee, and for the publication of clinical trial funds or other benefits. Specific clinical trials fall into the following categories: clinical trials that receive research funding or other benefits from the company; unapproved drugs, medical devices, regenerative medicine products, and approved drugs, medical devices, and regenerative medicine products Approved indications, dose-taking clinical trials. ASRM will be revised to ensure consistency with the Clinical Trials Act.
In general, if only immune cell collection and treatment performed in institutions such as clinics or hospitals, and clinical trials initiated by researchers, fall under the jurisdiction of the Regenerative Medicine Safety Law. If a third-party enterprise participates in the genetic manipulation, processing, preparation, production and sales of immune cells, it is under the jurisdiction of the Medicines and Medical Devices Act (the revised Pharmacy Law).
2
EU
The European Union incorporates tissue engineering, cell therapy, and gene therapy products into the management of Advanced Technology Therapeutic Medicine (ATMP), a drug that is defined as a revolutionary treatment for disease that has great promise for patients and industry.
There are two paths for the regulation of EU cell therapy: one is to conduct clinical research and declaration according to advanced technology therapeutic medical products, and is approved and managed by the European Medicines Agency (EMA); the second is to follow the hospital exemption clause, and the hospital decides on the patient. Therapeutic application.
From the legal level, the legal basis for cell therapy management is the EU Pharmaceutical Products Law and the Medical Device Law, which provides a legal regulatory framework for the pre-clinical research, clinical research, manufacturing and sales of pharmaceutical products across the entire industry chain.
With the rapid development of biotherapeutics, the EU has strengthened its supervision of cell therapy products. In 2007, the European Union issued the Regulation (EC) No. 1397/2007 on Advanced Therapy Medicinal Product, in 2008. Implemented on December 30th, the definition of gene therapy products, somatic cell therapy products and tissue engineering products as advanced technology therapeutic medical products, wherein cell therapy products refer to cells or tissues that have been treated to have changed biological characteristics, For the treatment, diagnosis or prevention of diseases. According to the drug declaration, the Advanced Technology Therapy Medical Committee approves and approves the time for 1~2 years. The hospital has introduced a hospital exemption clause (Article 28) that exempts a doctor from the treatment application behavior of the individual patient. This provision allows European hospitals to produce small-scale cellular products for specific patients, primarily clinical centers for autologous cell therapy, after basic research and clinical studies have validated efficacy and safety.
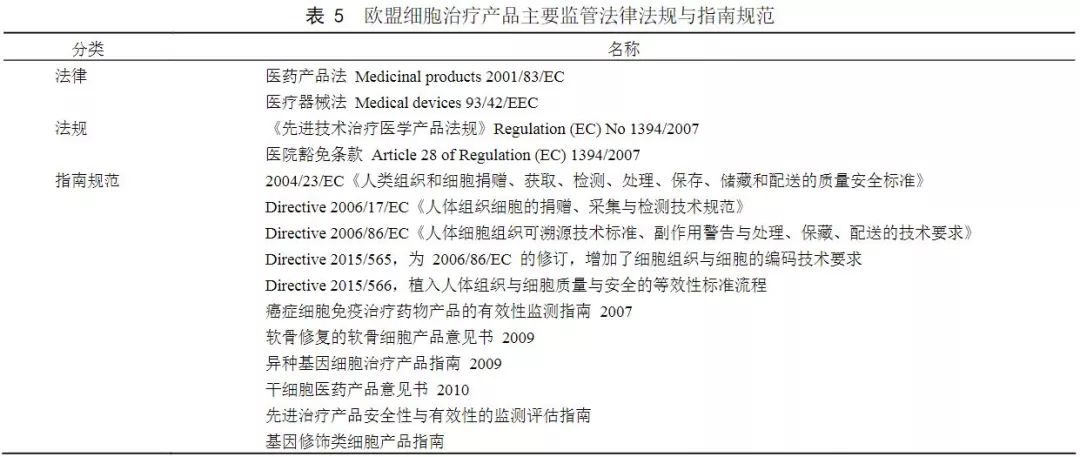
(Source: "China Medical Biotechnology")
In addition, the European Union has developed a series of scientific guidelines for gene therapy and cell therapy products . These guidelines address the development and regulatory requirements for ATMP, such as risk-based product development pathways and evaluation concepts, specific requirements for interactions between cellular and structural components, consideration of clinical/non-clinical flexibility, and Special requirements for Clinical Trial Management Practices (GCP), as well as special considerations for post-marketing safety effectiveness tracking and risk management.
In terms of the review process, the European Union mandated that the ATMP must implement a centralized review process and establish the Advanced Technical Therapy Committee (CAT), which is responsible for the technical review of new technology therapy products. CAT submits a review opinion to each ATMP submitted to management, but this opinion will be submitted to the Human Pharmaceutical Products Committee (CHMP), and CHMP will make recommendations for approval, change, suspension or cancellation of the marketing permit, and then Send the proposal to the European Commission for a decision. Once the product is approved for listing in the European Union, the management will further evaluate its safety and effectiveness. At the same time, in order to encourage the research and development of ATMP, the EU has implemented some special support and encouragement policies, such as reducing the part of the fees paid by the applicant to the management, and the applicant can obtain more scientific support and help from the EU.
In March 2016, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) launched a rapid approval program called PRIME, an experimental drug approved for PRIME, and will receive substantial support from EMA in clinical trials and medical development to accelerate real Approval of the development of innovative drugs to meet the medical needs of promising new drugs.
3
United States
The United States has formed a sound regulatory framework in the field of cell therapy, and its legal and regulatory system consists of three layers of laws, regulations, management systems and guidelines. Human cells, tissues, or cellular or tissue-based products (HCT/Ps) belong to the category of human tissues and cell products, and are classified into two categories: PHS 351 products and PHS 361 products. Management, PHS351 products are uniformly approved by the FDA's Center for Biological Product Evaluation and Research (CBER), and PHS 361 products can be directly used in hospitals for clinical applications.
Laws and Regulations From a legal perspective, the legal basis for cell therapy management comes from two Congressional Acts, the US Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C Act) and the Public Health Services Act (PHS Act) . The US Federal Regulations (CFR) are the basis for the establishment of FDA regulatory requirements. The most applicable regulations for stem cells are the requirements for submitting research-based new drug application requirements (21 CFR 312), as well as the regulations governing current drug production quality management practices (21 CFR). 210 & 211). The Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) is based on 21 CFR 210 and 211 of the CFR, the principles of which apply to stem cell products, including the physical characteristics of the equipment used to manufacture the product and the process of manufacturing the cell product in a device. And steps.
The United States issued the CFR1271 management regulations in 2001 and officially implemented it in 2005. This is the main basis for the approval of cell therapy. It divides human cell tissue into two major categories: PHS 351 and PHS 361. PHS 351 is a product of HCT/Ps classification, including bone, ligament, skin, dura mater. Heart valves, corneas, peripheral blood stem cells (PBSCs), cord blood-derived precursor cells, engineered autologous chondrocytes, epidermal cells on synthetic matrices, sperm or other reproductive tissues. The CAR-T products that have been approved in the United States are regulated under the PHS 351 product.
Guidelines and Regulations The FDA also communicates and interacts with other cell therapy authorities, companies, and research institutions, resulting in guidelines for manufacturing and clinical trials of most types of biological products. Among the many co-developed guidance documents, the defined principles apply to the evaluation of cell therapies. The formation of stem cell management recommendations is promoted between the FDA and NIH through the signing of a formal Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) agreement.
Approval regulatory framework The FDA Bioproducts Evaluation Research Center consists of the Office of Cell, Tissue and Gene Therapy, which consists of human tissue management, clinical evaluation and pharmacology, and cell and gene therapy . The Cell and Gene Therapy Department is responsible for receiving cell therapy. Product approval and access, the rapid approval process time is 6 to 10 months, and currently there are a variety of cell therapy products available in the United States.
PHS 361 cell therapy products do not require an IND application to the FDA, and are not classified as HCT/Ps products, including whole blood, blood components or blood-derived products such as white blood cells, platelets, blood clotting factors, etc. (regulated by blood product regulations) Minimization of cell-derived tissue, tissue or organ intervention, bone marrow for homologous applications, and the like.
PHS 361 products need to meet the following conditions: the preparation process is consistent with minimal intervention, only homology, no water, crystal liquid or any other reagents other than sterilization, storage and storage. And does not produce a systemic reaction, and does not depend on the metabolic processes of living cells; if a systemic reaction or a metabolic process dependent on living cells plays a role, it must be an allogeneic gene that is compatible with the 1st and 2nd grades of relatives. Transplant or as a reproductive application. The minimally manipulated product refers to the inability to change the relevant physiological characteristics (ie, without in vitro activation, encapsulation, amplification or genetic modification, etc.) during the processing of the cells.
4
China
In March 2003, the State Food and Drug Administration issued the "Guidelines for Human Cell Therapy Research and Preparation Quality Control Technology", requiring that the entire operation process and final product of each program must be developed and strictly implemented standard operating procedures to ensure the body Cell therapy is safe and effective.
In 2007, the National Development and Reform Commission, the Ministry of Health, and the State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine jointly issued the National Medical Service Price Project Specification, which regulates the cost of dendritic treatment (DC) and LAK cell therapy. In 2012, the specification was revised, and the price of the diagnosis and treatment services for tumor immunotherapy was uniformly regulated, which provided a legal basis for the collection of medical expenses. In terms of medical insurance, according to the new medical projects of the Ministry of Health, DK-CIK biological treatment has been included in the scope of the national medical insurance program, the provincial medical insurance can be reimbursed 90%, and the municipal medical insurance can be reimbursed 80%. This is a benefiting measure that cell therapy is used by the general public.
In March 2009, the Ministry of Health formulated and issued the “Administrative Measures for Clinical Application of Medical Technology†(Wei Zheng Zheng Fa [2009] No. 18), which stipulates that the third type of medical technology is responsible for technical certification and clinical application management by the Ministry of Health. The research institute confirmed that the animal test and clinical trial were effective, submitted the application to the Ministry of Health, and approved by the Ministry of Health for clinical treatment.
In May 2009, the Ministry of Health released the “First Class of Medical Technology Catalogues Allowing Clinical Applications†to categorize autologous immune cell (T cells, NK cells) treatment technologies into the third category of medical technology. For the first time, cell therapy technology has been used as a third type of medical technology, and since then, autoimmune cells (T cells, NK cells) have become more clearly managed.
In June 2009, the Ministry of Health formulated the "autologous immune cell (T cell, NK cell) treatment technology management specification for the clinical application of autologous immune cell (T cell, NK cell) treatment technology to ensure medical quality and medical safety. Opinion draft)). Management specifications have been developed for the treatment of autoimmune cells (T cells, NK cells), which has led to the availability of quality management rules for this technology.
In 2010, the Ministry of Health reviewed and approved the "Good Manufacturing Practices" (2010 Revision), implemented the concept of quality risk management and pharmaceutical production process management, and integrated with the World Health Organization's GMP regulations to become cells in the laboratory. The specifications that must be followed in the process. Production quality management needs more standards, and the integration with international GMP regulations marks that China's pharmaceutical production will be more stringent and achieve a transition from superior to excellent.
In June 2011, the Ministry of Health announced the list of the third category of medical technology audit institutions, including the Chinese Medical Association, the Chinese Hospital Association, the Chinese Medical Doctor Association, and the China Stomatological Association as the third category of medical technology audit institutions, valid from May 2011. 2nd to May 31st, 2013. The publication of the review body represents the certification of the authority.
In November 2011, the National “Twelfth Five-Year†Biotechnology Development Plan (Guo Ke Fa [2011] No. 588) clearly defined the following developments: “For malignant tumors, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, hereditary diseases, autoimmune diseases, etc. A major disease that seriously threatens human health, carry out a series of research on key technologies of targeted biotherapy such as targeted gene therapy, cell therapy, and immunotherapy, with key technology breakthroughs to drive the development of key products and accelerate the application of biotherapeutics to clinical applications. The speed of treatment.†Policy support at the national level, accelerating the application of biotherapeutic technology to clinical treatment is of great significance for national technological innovation and national health.
In December 2011, the Ministry of Health and the State Food and Drug Administration jointly issued the "Notice on Conducting Stem Cell Clinical Research and Application Self-examination and Self-correction Work" (Wei Ke Science and Education Letter [2011] No. 1177), and decided to jointly carry out the first phase. Year of stem cell clinical research and application activities. Conducting on its own and without any approval must stop immediately. For the clinical trial projects of stem cell products that have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration, they must be strictly implemented in accordance with the requirements of the quality specifications of the clinical trials of the approval documents and drugs. The clinical trial plan cannot be changed at will, and no charge can be made. At the same time, all new project declarations will be stopped by July 1, 2012. Industry chaos is frequent, and the healthy development of the industry requires the intervention of the regulatory authorities.
In July 2012, the Ministry of Science and Technology released the “Twelfth Five-Year†Biotechnology Development Plan, which included stem cell and regenerative medicine technologies, gene therapy and cell therapy technologies as development priorities. After the rectification of the industry into a benign development, the inclusion of development priorities represents the country's expectations for these technological breakthroughs.
In December 2012, the State Council issued a notice on the development of the property industry (Guo Fa [2012] No. 65) clearly listed anti-tumor drugs, therapeutic vaccines, cell treatments, etc. as important development and key support industries. The innovation of technology to promote the development of the industry, the key support will make the products produced by technology faster to be used by the public, which is the key policy of technology landing.
In 2013, the National Health and Family Planning Commission and CFDA jointly issued the “Methods for the Management of Stem Cell Clinical Trials (Trial)â€, “Management Methods for Stem Cell Clinical Trials and Research Bases (Trial)†and “Guidelines for Quality Control and Preclinical Research of Stem Cell Preparations†(Trial) The drafting of the three documents pointed out that the stem cell clinical trial research must be carried out in the stem cell clinical research base. The research base must have the requirements of the third-grade hospital and the drug clinical trial institution recognized by the drug regulatory bureau. For clinical trial management methods, research sites, and certification bodies, the clinical trials conducted by private individuals are nowhere to be seen.
In July 2015, the National Health and Family Planning Commission issued the National Health and Medical Development [2015] No. 71 "Notice of the National Health and Family Planning Commission on the Cancellation of the Third Class Medical Technology Clinical Application Approval Approval" clearly stated that "the third category was cancelled." After the medical technology clinical application is approved, the medical institution shall bear the main responsibility for the clinical application and management of the medical technology of the institution. All types of medical institutions shall follow the "Administrative Measures for Clinical Application of Medical Technology" (Wei Zheng Zheng Fa [2009] No. 18) Requirement, strengthen the sense of responsibility of the main body, establish and improve the clinical application management system of medical technology, perform surgical authorization and dynamic management of doctors according to the requirements of surgical grade management, and establish and improve the medical technology assessment and management file system." When the requirements and consensus of the industry are established, Strengthening the sense of responsibility of the main body makes supervision more flexible and will accelerate the development of the industry faster.
In 2016, it is a year of cell therapy. After the Wei Zexi incident in May, the National Health and Family Commission reiterated the ban and stopped all immune cell treatments being carried out in different hospitals across the country. On May 4th, the National Health and Family Planning Commission convened a video teleconference on standardizing the management of medical institutions and medical technology management. The meeting reaffirmed that autoimmune cell therapy technology is implemented in accordance with the relevant provisions of clinical research. The industry generally believes that this regulation further clarifies the industry standards for domestic immune cell therapy and regulates clinical applications, which is of great significance for promoting the healthy and sustainable development of the entire industry.
On December 16, 2016, since the publication of the "Guidelines for the Research and Evaluation of Cellular Products" (Draft for Comment), the cell treatment policy reflects the state's high support and encouragement for medical innovation technology, which will directly benefit cell therapy technology companies.
In December 2017, the CFDA issued the “Guidelines for the Research and Evaluation of Cellular Therapeutic Products (Trial)†to standardize and guide the research, development and evaluation of such products in accordance with drug management practices, and to develop these guidelines.
In 2018, on December 13, the National Health and Health Committee official website published a letter on the reply of the first meeting of the 13th National Committee of the CPPCC National Committee No. 4443 (No. 434 of Medical Sports). So far, there have been 102 medical treatments. The organization and 19 clinical research projects have completed the filing, enabling stem cell therapy technology to enter clinical research from basic research, and effectively promote the development of stem cell therapy technology in China. Drawing on the clinical research and management model of stem cells, the company will organize the research, selection and filing of clinical research institutions for cell therapy technology. Full support for cell therapy products to declare drug registration.
Biomedical New Technology Clinical Application Management Regulations
(1) Clarify the scope of management. The Ministry of Science and Technology is responsible for drafting the "Regulations on the Safety Management of Biotechnology Research and Development" and standardizing the basic research of biotechnology. This regulation regulates the clinical phase of biotechnology research and transformation applications. According to this, the new biomedical technology is defined as: pre-clinical research has been completed, which is intended to be at the cellular or molecular level to judge or prevent diseases, eliminate diseases, alleviate the disease, relieve pain, improve function, prolong life, Medical professional tools and measures to help restore health and other purposes.
(2) Established an administrative examination and approval system for clinical research and transformation application of biomedical new technologies. First, it is required that the medical institutions carry out clinical research and transformation applications of biomedical new technologies must be approved by the administrative department. The second is to stipulate the conditions for carrying out the biomedical new technology clinical research medical institutions and the main person in charge of the project. The third is to clarify that the approval of the health administrative department is based on academic review and ethical review. Fourth, the clinical research on new biomedical technologies is managed at two levels according to the risk level. The low- and medium-risk research projects are examined and approved by the provincial health authorities, and the high-risk research projects are reviewed and approved by the provincial health authorities. The application for the transformation of results is the responsibility of the competent health department of the State Council.
(3) The main contents of academic review and ethical review are prescribed. Drawing on the relevant provisions of the international and World Health Organization ethical review, the regulations stipulate the main contents of the academic review and ethical review of the health authorities, and enhance the seriousness and standardization of the review. At the same time, the regulations for review, including the composition of ethics committees and academic committees, the review of specific technical specifications, and the conclusions of the review, shall be formulated separately.
(4) Emphasize the main responsibility of the institution. Medical institutions that explicitly carry out (including lead or participate in) clinical research assume the primary responsibility. Medical institutions that explicitly carry out clinical research should have certain conditions, and specific conditions should be formulated separately. The main person in charge of the medical institution is the first person responsible for the clinical research management of the institution. The medical institution provides technical support and research sites for other institutions, provides samples of human cells, tissues, organs, etc., and assists in the recruitment of volunteers. The institution and the participants also bear corresponding responsibilities.
(V) Increased penalties for violations. In view of the weak penalties imposed by the existing regulations, the problem of deterrence cannot be formed, and the regulations have increased the penalties for violations. Punishment measures, including warnings, deadline corrections, fines, cancellations, etc., are clarified for cases where medical institutions violate clinical regulations and conversion applications, conduct research according to regulations, violate regulations by physicians, violate regulations of other medical personnel, and conduct non-medical institutions to conduct clinical research. Medical treatment subjects, revocation of the "medical institution practice license", expulsion or dismissal, lifelong biomedical new technology clinical research, etc.; serious cases will also be investigated for criminal responsibility.
(6) Linking with the management of medicines and medical devices. The expected results of some biomedical new technology clinical research are drugs or medical devices, and the regulations are regulated in accordance with the Drug Administration Law and the Regulations on the Supervision and Administration of Medical Devices.
Interpretation of the Clinical Research and Transformation Application Management Method for Somatic Cell Therapy (Trial):
The scientific definition of somatic cells includes stem cells. The former National Health and Family Planning Commission and the former General Administration of Food and Drug Administration issued the "Cell Cell Clinical Research Management Measures (Trial)" in 2015, effectively regulating and promoting the clinical research work of stem cell therapy in China. Management Measures “Article 31, somatic cell therapy with special management methods shall be implemented in accordance with current regulationsâ€, and relevant work on stem cell clinical research is still carried out in accordance with the provisions of the “Cell Cell Clinical Research Management Measures (Trial)â€.
Article 3 of the Administrative Measures stipulates that “the present Measures shall apply to clinical research and transformation applications of somatic treatment developed, prepared and carried out in medical institutions by medical institutionsâ€. The National Health and Health Commission carried out catalogue management of cell therapy conversion application projects, and misaligned the development of cell therapy products with obvious industrialization prospects. The somatic cell treatment products researched and developed by the enterprise shall be reported to the national drug regulatory authority for registration and listing in accordance with the relevant provisions on drug administration.
In accordance with the relevant provisions of the Administrative Measures, medical institutions that carry out clinical research and transformation applications for somatic treatment should be filed. When the medical institution conducts the first institutional filing, it must also provide medical institution filing materials and clinical research project filing materials.
The study of somatic cell therapy should not charge the subject any research-related costs. The somatic cell therapy conversion application project can be transferred to clinical application after being filed. The medical institution applying for filing shall follow the notice of the National Development and Reform Commission and other four departments on the issue of proposing the reform of medical service price reform (Development and Reform Price [2016] No. 1431) For the relevant requirements, apply for a fee to the local provincial price authority.
5
to sum up
The above is the regulation of multinational cell therapy, and there are indeed different places. Whether the regulatory principles and methods can boldly draw on some of the advantages of the international community and improve the regulatory system in combination with our own practices. Since the end of 2017, CAR-T cells, TCR-T cells, stem cells, and DC vaccines have been accepted and approved in accordance with the declaration and review of drugs. Whether the road for innovative review that has just begun is still in the process of development.å˜åœ¨å¾…需完善的机制,是å¦å¯ä»¥ç»“åˆè¯ç›‘部门对è¯å“注册审评的ç»éªŒå’ŒåŒ»ç–—æœºæž„è‰¯å¥½çš„ä¸´åºŠç ”ç©¶å’Œä¼¦ç†ç»éªŒè¿›è¡Œä¼˜åŠ¿æ•´åˆï¼Œä»Žè€Œä¿è¯ä¸åŒæ¥æºçš„细胞制å“都有éžå¸¸å¥½çš„安全性和疗效评估ä¿éšœã€‚
当然我们有自己特殊的国情,所以éžå¸¸ç†è§£ä¸Žæ”¯æŒä»Žä¸¥ç›‘ç®¡çš„ç›®æ ‡ä¸Žå‡†åˆ™ã€‚å¸Œæœ›å¤šå¬å–å„方建议,科å¦ä¸¥è°¨ä½†ä¸å¤±åˆ›æ–°çš„æ€åº¦ç»§ç»ä¸ºæŽ¨åŠ¨ä¸å›½ç»†èƒžæ²»ç–—产业å¥åº·å‘展共åŒåŠªåŠ›ã€‚
å‚考出处:
美国ã€æ¬§ç›Ÿã€æ—¥æœ¬ç»†èƒžæ²»ç–—监管政ç–ç ”ç©¶, 《ä¸å›½åŒ»è¯ç”Ÿç‰©æŠ€æœ¯ã€‹2016å¹´12月第11å·ç¬¬6期
https://
客觀日本:细胞治疗与å†ç”ŸåŒ»ç–—,ä¸æ—¥ç›‘管大ä¸åŒï¼ˆä¸Šï¼‰ï¼ˆä¸‹ï¼‰
https://cdn.ymaws.com/
https://(18)30552-6/fulltext
https://
Industrial Gelatin,Industrial Hide Gelatin Powder,Industrial Gelatin For Woodworking,Industrial Gelatin For Abrasive Paper
Hebei Haodong Biological Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.hdgelatin.com