Progress in research and development of new antiviral chemistry drugs: cure ideal VS short drug reality
April 13, 2015 Source: Medical Network
Window._bd_share_config={ "common":{ "bdSnsKey":{ },"bdText":"","bdMini":"2","bdMiniList":false,"bdPic":"","bdStyle":" 0","bdSize":"16"},"share":{ }};with(document)0[(getElementsByTagName('head')[0]||body).appendChild(createElement('script')) .src='http://bdimg.share.baidu.com/static/api/js/share.js?v=89860593.js?cdnversion='+~(-new Date()/36e5)];
Medical Network April 13th The development of antiviral drugs is still a worldwide medical problem, and there are only a handful of viral infectious diseases that can be cured by drugs, often relying on its own immune system to clear. In addition, the anti-viral new compounds have a phase-out rate of more than 70% after Phase I to III clinical trials, resulting in relatively new broad-spectrum antiviral drugs on the market, such as lamivudine tablets with specific indications. Viral drugs are still scarce.
In contrast to this is the incidence of various viral diseases continues to increase. According to the latest WHO data, there were approximately 35 million people living with HIV in 2013 and 2.1 million new infections. In terms of hepatitis, more than 240 million people worldwide suffer from chronic (long-term) liver infections. About 780,000 people die each year from acute or chronic hepatitis B, and 130 million to 150 million people suffer from chronic hepatitis C infection. 10,000 to 500,000 people died of liver diseases associated with hepatitis C. The flu virus is also ravaged by the whole world. Only seasonal flu kills 250,000 people every year in the world, and SARS, avian flu, and influenza A are frequently mutated.
CDE New Drug Overview: Low Position
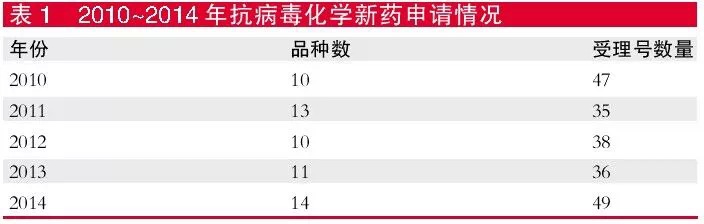
In the past five years, the number of applications per year has not exceeded 15 , and the number of acceptances has not exceeded 50 .
According to the CDE review data, in the past five years, the number of new antiviral chemical drugs applied by CDE has been relatively stable. The number of new drug applications per year has not exceeded 15, and the number of acceptance has not exceeded 50. In 2014, there were only 49 acceptance numbers, involving 14 varieties.
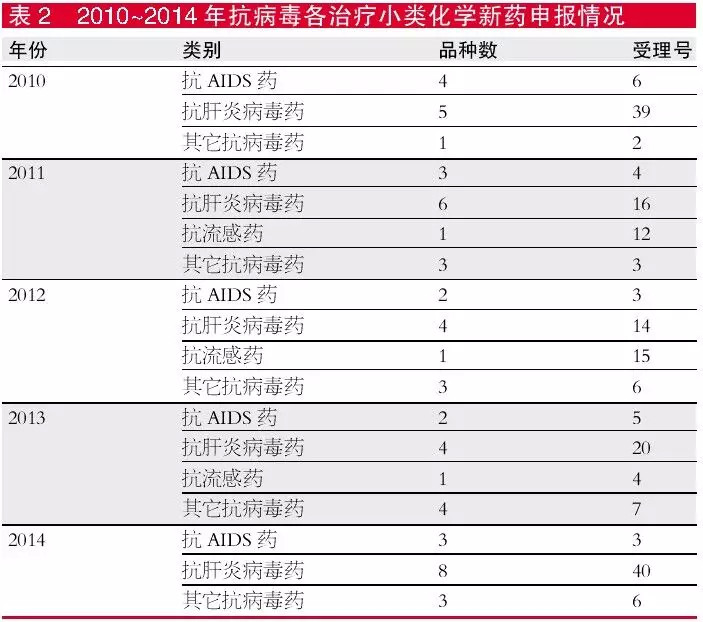
From the perspective of treatment subcategories, the application of new chemical drugs in the past five years has mainly focused on anti-hepatitis virus drugs. In 2014, the number of varieties was the highest, with 7 and the number of acceptance numbers was 38. Anti-AIDS varieties range from 2 to 4, and the acceptance number is also less than 6. The anti-influenza species began to have only one variety per year in 2011, and in 2014 there was no corresponding new drug variety declaration.
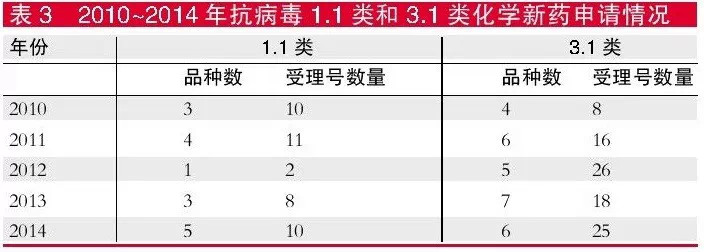
In terms of registration type, the number of anti-virus 1.1 new chemical drugs in the past five years is small, the number of varieties is less than 4, the number of acceptance numbers is not more than 11, and the number of new types of 3.1 drugs is also less, and the number of varieties is less than 7. However, there are more acceptance numbers, from 8 in 2010 to 25 in 2014.
Anti-AIDS drugs: 2 classes of 1.1
In addition to the 1.1 class of eftstatin and Azovudine, the 3.1 class of efavirenz and the 3.2 class of lamivudine tenofovir are exclusive declarations.

From 2010 to 2014, there were only two types of 1.1 new anti-AIDS chemical applications, namely Affitta, which was applied for by the Tianjin Pharmaceutical Research Institute in 2011, and Azfudine, which was applied for by Zhengzhou University in 2013. Azfj is the world's leading and domestically pioneered new generation of AIDS drugs. It is currently in a leading position in the world. Its activity is much better than the listed anti-AIDS drugs (such as 3TC, etc.), and its toxicity is much smaller.

There were only one 3.1 and two 3.2 categories of new drugs applied in 2014 and all were exclusively declared. Among them, the 3.1 new drug efavirenz was used as the first-line drug for AIDS. The original drug was Merck's Stony, and the global sales scale was about 800 million US dollars. The 3.2 new drug lamivudine tenofovir tablets is used to treat AIDS with chronic viral hepatitis B. Both lamivudine and tenofovir are nucleoside (acid) anti-reverse enzyme inhibitors, both of which inhibit human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and hepatitis B virus (HBV). Because patients have better tolerance to lamivudine, lamivudine is a first-line antiviral drug for patients with AIDS complicated with chronic viral hepatitis B, but it has a higher incidence of drug resistance. Studies have shown that tenofovir has a good inhibitory effect on wild-type HBV strains and lamivudine-resistant strains. For chronic hepatitis B, combination therapy may play a better role in inhibiting the virus and reducing the incidence of drug resistance, especially in patients with HIV infection.
Anti-hepatitis drugs: 11 1.1 classes Hepatitis B drugs focus on adefovir dipivoxil and tenofovir disoproxil; hepatitis C drugs are mainly NS3/4A inhibitors, focusing on NS5A and NS5B inhibitors.
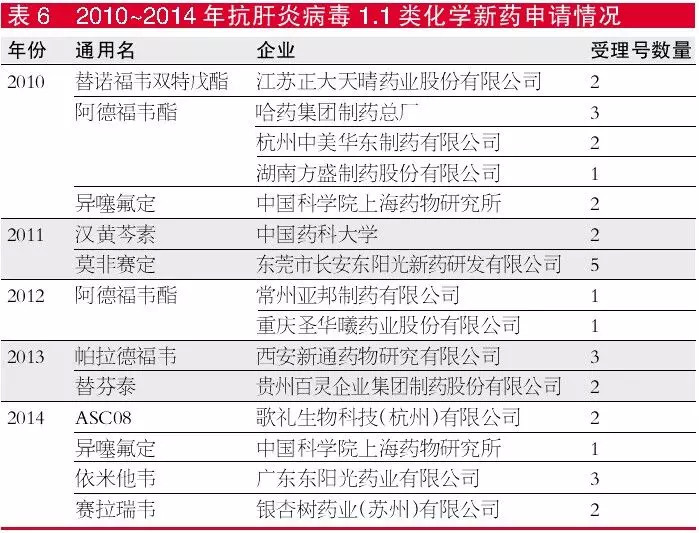
From 2010 to 2014, there were 11 types of 1.1 new anti-hepatitis virus chemical applications, of which adefovir dipivoxil in 2010 and 2012 a total of 5 manufacturers declared 1.1 new drugs. Adefovir dipivoxil (trade name: Mingzheng) independently developed by Jiangsu Zhengda Tianqing was approved for production in 2006 and is a listed product with independent intellectual property rights. Adefovir dipivoxil is indicated for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B, especially for those who need long-term medication or who have developed lamivudine resistance, and thus become one of the anti-hepatitis varieties that manufacturers are competing to develop.
At present, chronic hepatitis B is the most common disease in China. However, due to the limited economic affordability of many domestic families, it is difficult to bear expensive antiviral drugs, so the relatively low price of lamivudine and adefovir. Ester still occupies a considerable proportion of the market share, and domestically produced high-quality and high-priced drugs are an important choice for patients.
Tenofovir is a novel nucleotide-based reverse transcriptase inhibitor approved by the US FDA in October 2001 and 2008 for the treatment of AIDS and hepatitis B (CHB). Tenofovir has been approved for the treatment of AIDS in more than 100 countries including China, and more than 30 countries and regions such as the United States have received indications for the treatment of hepatitis B with tenofovir. Tenofovir is the nucleoside (acid) drug with the strongest anti-hepatitis B virus (HBV) activity and the highest drug resistance barrier. Clinical studies have shown that it has good antiviral effect on HBV, HBV and HIV-infected patients. The AASLD (American Society for the Study of Liver Diseases) guidelines, updated in 2009, recommend tenofovir as a first-line treatment for CHB antiviral therapy. In 2010, tenofovir obtained a new Chinese drug trial for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B, marking a new stage in the registration of tenofovir, a new drug for chronic hepatitis B antiviral therapy in China.
Organic Tapioca Resistant Dextrin Syrup
Resistant Dextrin Prebiotic, Organic Soluble Dextrin,High Ingredient Tapioca Fiber,Low Calorie Soluble Fiber
Shandong Bailong Chuangyuan Bio-tech Co.,Ltd. Qingdao Branch , https://www.sdblcycn.com