At this stage, domestic enterprises engaged in medical artificial intelligence are surging, and most of them are based on the video reading work of medical technology departments. Many companies have a single product and the homogenization phenomenon is more serious.
However, as the core of the hospital, the clinical department is directly related to medical quality and patient health. In these enterprises, the companies that serve the clinical departments belong to the minority. The SI Group network is one of them directly serving the tumor. An innovative company with a doctor's purpose.
Artificial intelligence is the foundation of personalized medicine
Personalized medicine is also known as precision medicine: it is based on the patient's personalized information, including clinical and various omics information, and is designed to best for patients through medical decision-making, practice and interventions. Treatment options to achieve a customized medical model that maximizes treatment effectiveness and minimizes side effects.
At this stage, personalized medicine or precision medicine has become a hot spot in the world's medical industry. International pharmaceutical giants have long used personalized diagnosis and treatment as the direction of research and development.
In general, personalized medicine includes two aspects:
First, personalized diagnosis and evaluation: mainly involves the integration of a variety of information, relying on molecular diagnostic technology, clinical big data and cloud computing technology. At present, because molecular level omics data is still not perfect, better use and mining of clinical data is also an important part of precision medicine. Through the collection and detection of individual patient related information, the relevant diagnosis and evaluation results are obtained. For complex situations that need to integrate multiple factors, it is also dependent on artificial intelligence technology such as data mining algorithms.
The second is personalized treatment: individualized treatment can be applied to patients according to the assessed risks, and “quantitative medicine†can be realized.
According to Dr. Tao Ying, the chief artificial intelligence officer of Sipai Network, the realization of personalized medicine requires at least three factors:
1. Clinical guidelines;
2. Individualized data of individualized patients;
3. Artificial intelligence algorithms and models.
Clinical guidelines provide a basic decision-making reference for personalized medicine. Currently, various countries, disciplines, and societies have published various treatment guidelines and consensus on disease treatment. Guidelines and consensus are directed at the treatment of a particular disease or the use of a particular drug, based on current research evidence, and the ideas and opinions formed to guide the general practitioner's clinical practice.
Often, clinical guidelines are for a patient population and are generally broad. Because each patient's condition is different, the clinical guidelines do not give a clear, personalized approach that covers all patients. Some uncommon situations are often inadequately covered, such as elderly patients with multiple complications at the same time.
At present, in most cases, doctors who do not cover the guidelines need to be personalized according to their own experience. However, there are many problems in this way, including the experience of doctors may not be sufficient, and the probability of integrating various factors to accurately and scientifically calculate various risks is very difficult for human doctors.
In this context, combined with the actual data of patients, mathematical modeling through machine learning and other algorithms, using mathematical models to assess patients' risk, and finally form clinical decision-making, has become an important direction to assist doctors in personalized medicine.
How to build a personalized forecasting model?
According to Dr. Tao, Sipai Network is developing a risk prediction for adverse reactions caused by cancer chemotherapy. The project is named "Sherlock Holmes". Dr. Tao also said that the establishment of a personalized predictive model requires the following steps:
First, it is necessary to determine the content of the prediction, the medical problem to be solved; and then collect the actual data of the individual patient according to the predicted content, instead of the statistical data of the group. So far, the company has established a tumor database of about 450,000 patients. The data comes from more than 700 oncology-related departments in more than 300 hospitals.
After the database is formed, the next step is to clean and model the data, including selecting some data algorithms, and repeatedly optimizing the model parameters according to the algorithm, so that the model has the best prediction effect, for example, the area under the ROC curve (AUC) is the largest.
Taking the chemotherapeutic nausea and vomiting prediction model as an example, the database collected by the model includes 12,000 lung cancer patients, 23292 systemic treatment cycles, and 19 tumor-related departments across 12 provinces. After several rounds of testing, the final selection was made. The most generalized and robust naive Bayesian algorithm for statistical analysis.
This algorithm can give a more accurate risk probability. Based on this probability combined with clinical guidelines, doctors can give personalized chemotherapy and vomiting prevention programs.
For example, patients with a risk greater than 90% need to be given three antiemetics, and patients with a risk of less than 10% may not be administered, and one or two drugs may be given between the two, such personalized treatment It can prevent the occurrence of adverse reactions to the greatest extent, while avoiding over-medication.
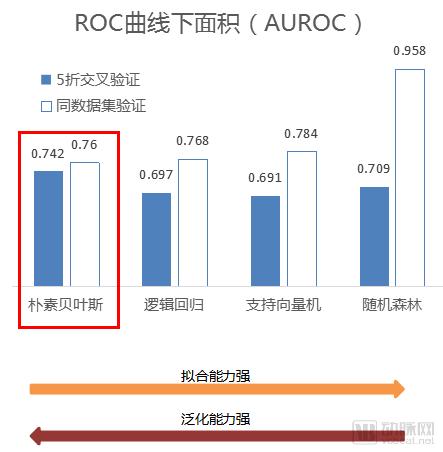
For the evaluation of the model, if it is a two-class problem, the most commonly used method is the area under the ROC curve, with the true positive rate (sensitivity) as the ordinate and the false positive rate (1-specificity) as the curve plotted on the abscissa.
In general, the area under the ROC curve is between 1.0 and 0.5. In the case of AUC > 0.5, the closer the AUC is to 1, the better the diagnostic effect. AUC has lower accuracy from 0.5 to 0.7, AUC has a certain accuracy from 0.7 to 0.9, and AUC has higher accuracy at above 0.9. When AUC=0.5, it means that the diagnostic method is completely ineffective and has no diagnostic value. AUC<0.5 does not match the real situation and rarely occurs in practice.
When the model is initially built, the model needs to be verified in the real scene of the hospital to determine the final model. During this process, the model may also have some problems with overfitting. Thanks to the large amount of data, the current AUC of the chemotherapeutic nausea and vomiting model in the hospital has reached 0.87, which is a high level in the industry.
See below:
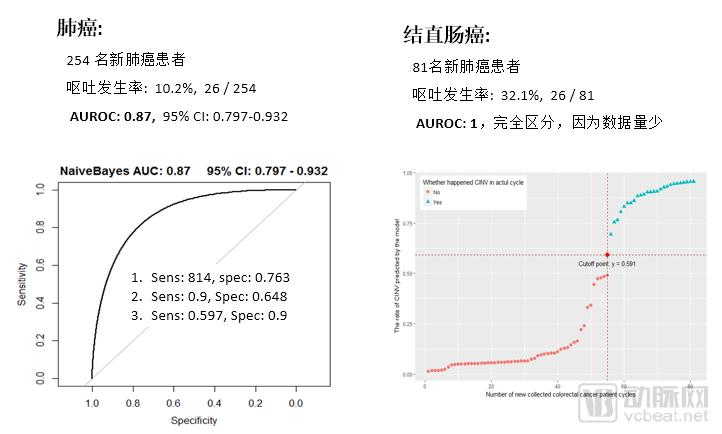
Due to the small number of cases of some tumors, Spiegel is mainly designed for some large cancer types such as lung cancer and colon cancer. According to reports, in addition to chemotherapy nausea and vomiting adverse reactions, Sipai is also developing a more predictive model of myelosuppression induced by chemotherapy for doctors and patients, and has obtained relatively good preliminary results, which is still to be further verified in the hospital scene. .
Sipai's decision-making tools mainly rely on WeChat public number and APP for product development and verification. At present, the WeChat public number platform has been used by more than 1,000 doctors. As long as you are a user of the Spiders database, you can open the APP product. For doctors, this is equivalent to opening a "mobile database."
Can artificial intelligence products be used clinically?
Can artificial intelligence be applied to personalized medicine in clinical departments at this stage? The most vocal, is a clinician. In this regard, the arterial network interviewed two oncologists in the top domestic hospitals, hoping to get answers to the questions from them.
According to Cui Chuanliang, deputy director of the Department of Cardiovascular Melanoma, Peking University Cancer Hospital, the current treatment of cancer is divided into three categories: immunotherapy, targeted therapy and traditional chemotherapy.
When choosing a treatment plan, doctors first determine the direction of treatment and determine whether to use immunotherapeutics, targeted drugs or traditional chemotherapy. After the direction is determined, the doctor will select some specific drugs according to the patient's organ function, the transfer position and the adverse reactions of the drugs.
In this process, the role of clinical guidelines is to choose the direction of the drug, such as which type of patient is suitable for immunotherapy or targeted therapy and chemotherapy, and then the doctor combines some individualized indicators of the patient, such as site mutations, targets Point, organ function, whether there are contraindications to treatment, etc., finally choose the type, dose and course of treatment or treatment.
In this regard, Zheng Yulong, deputy director of the Department of Oncology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, gave the same answer. He believes that in the treatment of cancer, the clinical guidelines can only give the doctor a reference role, and the specific treatment methods need to be personalized according to the patient's liver and kidney function, genetic data and other differential data.
According to the arterial network, the scope of application of drugs is generally judged according to the level of evidence. If a drug has a high level of evidence for a certain type of patient, the doctor will only need to use the patient at the recommended dose and course of treatment. In general, the higher the level of evidence, the more likely it is to be added to the instructions for use of the drug.
For this reason, the instructions given often are the recommended dosage and range of the drug, but the scope of treatment of the drug is generally wider, and many indications have not been written into the specification. Only when there is clear evidence of RCT test can a doctor choose it as a treatment for a disease.
Once the patient has an adverse reaction during the treatment of the tumor, the doctor will make different treatments according to the degree of toxicity. In general, mild (grade 1) and moderate (grade 2) adverse reactions can continue to be observed. If it is a serious adverse reaction, such as severe (level 3), potential life threat (level 4), it will be discontinued or reduced.
“Usually, we are involved in pretreatment during the treatment process, such as taking the patient's precautionary antiemetic drugs according to the patient's condition and economic conditions.†Director Cui said.
Because some doctors have less experience in adverse reactions, it is likely to miss rare adverse reactions or treat them for other reasons.
In this regard, Director Zheng said: "If the artificial intelligence system can prompt rare adverse reactions, it will allow clinicians to more fully consider the patient's medication and treatment."
For the application of personalized diagnosis and treatment of artificial intelligence products, the two directors put forward deep thinking:
Director Zheng believes that artificial intelligence products must be able to reflect the actual situation of patients, so the accuracy of the model and the authenticity of the data are very important. Due to the relative fragmentation of hospital data at this stage, the disease record alone cannot fully reflect the patient's specific situation, and it is necessary to add data such as follow-up and genome to ensure the credibility of the results.
Director Cui believes that the current artificial intelligence model is more suitable for routine patient treatment to ensure that doctors do not make big mistakes. However, for some diseases with a small number of cases, due to the lack of sample size, even if the prediction results are given by the model, it is difficult for doctors to draw conclusions based on it, so it may not be suitable for cutting at this stage. Therefore, companies can first test whether a model can accurately predict the efficacy and adverse reactions of a drug by strictly observing a group of patients.
Hospitals, doctors, pharmaceutical companies, patients benefit from multiple parties
According to Tao Ying, the company's artificial intelligence products mainly serve hospitals and pharmaceutical companies, and patients are the ultimate beneficiaries.
The hospital's needs are to help doctors make decisions based on risk prediction criteria, to help medical staff prevent and treat patients' adverse reactions during chemotherapy and drug treatment, and to reduce unnecessary medication or medication omissions.
For pharmaceutical companies, the more adverse reactions caused by drugs, the more unfavorable the market for drugs.æ€æ´¾'s artificial intelligence products can promptly report, report and reduce the occurrence of adverse reactions.
In addition, the use of artificial intelligence can also improve patient compliance with drugs. For example, before a patient develops nausea or vomiting, the doctor can prescribe the patient to take some antiemetic drugs according to the risk prediction, reduce the possibility of stopping the drug, and ensure the efficacy of the drug.
In addition, the Pioneer's predictive model can also be used to determine contraindications for new drugs. Through the model analysis, it is suggested that the type of patients in the enterprise have a large adverse reaction, so as to update their product manual.
For each of the cooperative hospital departments, Sipai will send data entry personnel to help doctors collect and organize data. Every patient's data obtained by the school will be desensitized by the hospital, so it does not contain any sensitive information of the patient.
Tao Ying revealed to the arterial network that Sipai will position the tumor-related department instead of the current hot image or pathology department because the company believes that the clinical department is the core of the hospital and is optimistic about the application of artificial intelligence in clinical departments.
Hydrophilic Reinforcement SM Nonwoven
SMS Nonwoven,Non Woven SMS Fabric,SMS Non Woven Fabric,Disposable SMS Nonwoven
ShaoXing SurgeCare Medical Products Co., Ltd. , https://www.sxsurgecaremedical.com